In an environment of cut-throat competition, it would be a bad idea not to include web scraping as a marketing and monitoring strategy to keep check on your competitors. Extracting publicly available data not only provides you with competitive leverage but also empowers you to make astute strategic decisions to expand your foothold in the market.
In this tutorial, we will be scraping Google Shopping Results using Python. We will also explore the benefits and solutions to the problems that might occur while gathering data from Google Shopping.
Why Scrape Google Shopping?
Google Shopping, formerly known as Google Product Search or Google Shopping Search, is used for browsing products from different online retailers and sellers for online purchases.
Consumers and retailers benefit from Google Shopping, making it a valuable e-commerce tool. Consumers can compare and select different ranges of products, while it helps retailers by increasing their discoverability on the platform and potentially driving more sales.
Read More about it here.
Scraping Google Shopping is essential if you want to avail the following benefits:

Price Monitoring – Scraping data from Google Shopping to monitor the pricing of a product from multiple sources, and compare them to get the cheapest source, to save customers money.
Product Information – Get detailed information about the products from Google Shopping, and compare their reviews and features with various other products to find the best from them.
Product Availability – You can use Google Shopping data to monitor the availability of a set of products instead of manually checking the product from different sources, which consumes your valuable time.
Understanding Google Shopping and Product Page
Before extracting data from the Google Shopping page, it is important to understand its structure. The below image includes all the data points for the Google search query “Samsung Galaxy”.
Search Page
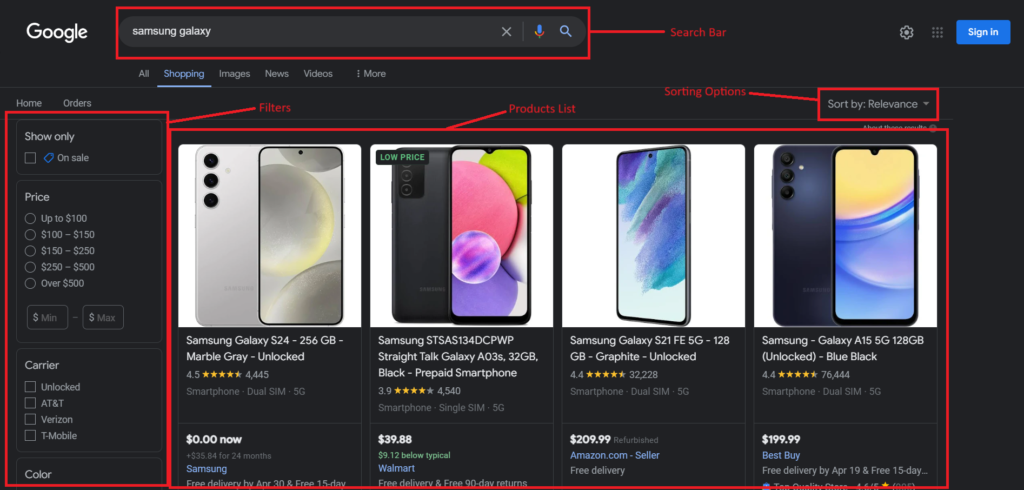
Products List — It consists of the products from various online retailers relevant to the search query.
Filters — It allows you to refine search results based on color, size, rating, etc.
Sorting Options — It allows you to sort products based on pricing, customer ratings, etc.
Finally, the products under the list, consist of titles, pricing, ratings, reviews, sources, and much more as the data points.
Product Page
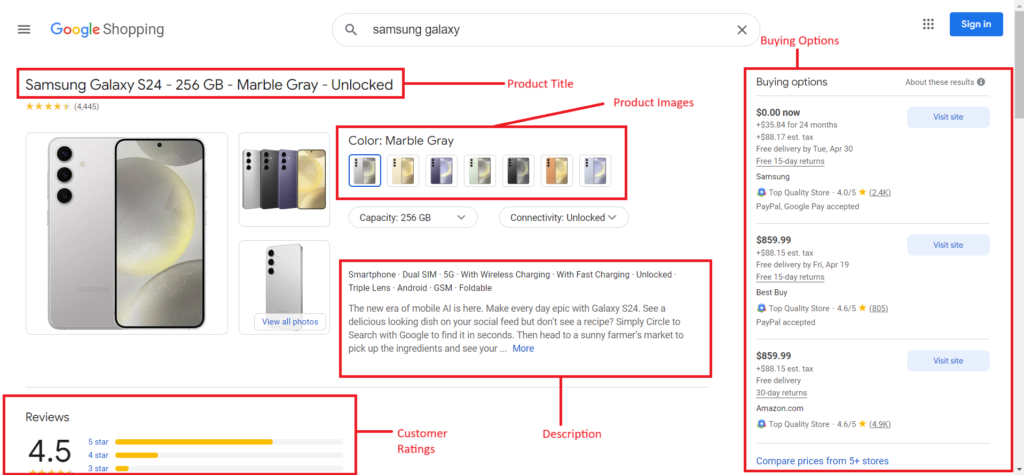
Navigating the product page gives you detailed information about the product:
- Product Title
- Pricing
- Rating and Reviews
- Features
- Description
- Buying Options
Scraping Google Shopping results Using Google Shopping API
In this section, we will be scraping Google Shopping Results using Serpdog’s Google Shopping API. But let us first complete the requirements for this project.
Install Libraries
To scrape Google Shopping Results we need to install an HTTP library so we can move forward.
So before starting, we have to ensure that we have set up our Python project and installed our packages— Requests. You can install the packages from the above link or run the below command if you don’t want to read the documentation.
pip i requests
API Key From Serpdog
As we are using Serpdog’s Google Shopping Scraper for this tutorial, we would also need an API Key to extract the shopping results.
Getting an API Key from Serpdog is easy. You have to register on its website, and after that, you will be directed to its dashboard where you will get your API Key.
Process
Search Page
It is a great practice to decide in advance which entities are required to scrape before starting anything. These are the following data points which we will cover in this tutorial:
- Title
- Rating
- Reviews
- Pricing
- Source
Since we have completed the setup, we will import our previously installed libraries and define the parameters to be passed with the API request.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
payload = {'api_key': 'APIKEY', 'q':'nike+shoes' , 'gl':'us'}
resp = requests.get('https://api.serpdog.io/shopping', params=payload)
print (resp.text)
We have used only a few geolocation parameters. However, you can also add more parameters by reading this documentation to personalize the results. And don’t forget to put your API Key in the above code.
Run this program in your terminal to obtain the shopping search results.
{
"meta": {
"api_key": "APIKEY",
"q": "shoes",
"gl": "us"
},
"filters": [
{
"type": "Price",
"options": [
{
"text": "Up to $30",
"tbs": "mr:1,price:1,ppr_max:30"
},
{
"text": "$30 – $50",
"tbs": "mr:1,price:1,ppr_min:30,ppr_max:50"
},
{
"text": "$50 – $70",
"tbs": "mr:1,price:1,ppr_min:50,ppr_max:70"
},
{
"text": "$70 – $100",
"tbs": "mr:1,price:1,ppr_min:70,ppr_max:100"
},
....
The results will include the search filters and the list of products as shown on the Google Shopping Page. However, the above response is not complete as it is not possible to show the complete data here.
If you want to get only the list of products from the scraped data then we have to make small customizations in the code.data = resp.json()
print(data[“shopping_results”])
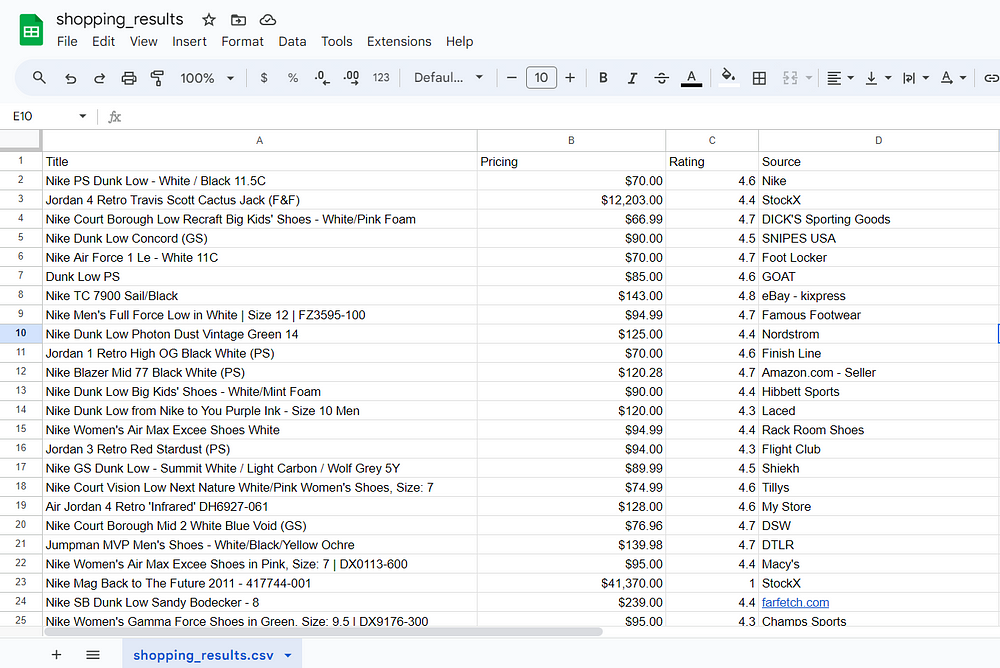
Exporting the list of products to CSV
Finally, we will export the list of products to a CSV file. We will get the product title, pricing, rating, and source from the extracted data. Here is the complete code to get the output in a CSV file.
import requests
import csv
payload = {'api_key': 'APIKEY', 'q':'nike+shoes' , 'gl':'us'}
resp = requests.get('https://api.serpdog.io/shopping', params=payload)
data = resp.json()
with open('shopping_results.csv', 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
# Write the headers
csv_writer.writerow(["Title", "Pricing", "Rating", "Source"])
# Write the data
for result in data["shopping_results"]:
csv_writer.writerow([result["title"], result["price"], result["rating"], result["source"]])
print('Done writing to CSV file.')
After opening the CSV file shopping_results.csv we placed the headers title, pricing, rating, and source on the top. After that, we loop through each shopping result and write the corresponding data title, pricing, rating, and source to the CSV file using csv_writer.writerow.
Running this program will return you a CSV file as an output.
Conclusion:
Google Shopping is the most trouble-free spot when attempting to retrieve data from multiple e-commerce sources. It aids in monitoring consumers and competitors, enabling data-driven, informed decisions, and helping your business in its growth efforts.
I hope this tutorial gave you a clear understanding of why it is beneficial for businesses to scrape shopping results.
Feel free to message me anything you need clarification on. Follow me on Twitter. Thanks for reading!
Additional Resources
- How to scrape Google Organic Search Results using Node JS?
- Scrape Google Images Results
- Scrape Google News Results
- Scrape Google Maps Reviews

