Bing is one of the major search engines currently in use today. With a 15% market share in the US, it is the second largest search engine company after Google. Bing contains tons of valuable data that can be utilized for market trends, SERP monitoring, media monitoring, etc.
In this tutorial, we will learn to scrape Bing search results using Python and its libraries. We will also explore the benefits of extracting data from Bing and why the official Bing Search API may not be the best to gain access to Bing search results.
Why Scrape Bing?
Scraping Bing can provide you with various benefits:
SERP Monitoring — It can help you monitor your website rankings on the search engine, which then, can be used to improve your website rankings according to the algorithm.
News Monitoring — Monitor the news around the globe by collecting data from Bing and use this data to analyze various trends and sentiments.
Lead Generation — Scrape the Bing data to enrich any company employees’ database and sell them at a profitable price in the market.
Setting up our Scraper
In this section, our main objective is to extract the initial 10 search results from Bing, which include titles, links, and descriptions (snippets).
Installing Python
To install Python on your device, you can consider the below videos:
If you don’t want to watch videos, you can directly install Python from their official website.
Requirements
To scrape Bing, we will be using these two Python libraries:
- Beautiful Soup — Used for parsing the raw HTML data.
- Requests — Used for making HTTP requests.
You can run the below commands in your project terminal to install the libraries.
pip install requests
pip install beautifulsoup4
Process:
Okay, so we are done with the setup. Next, we will scrape the data from this page.
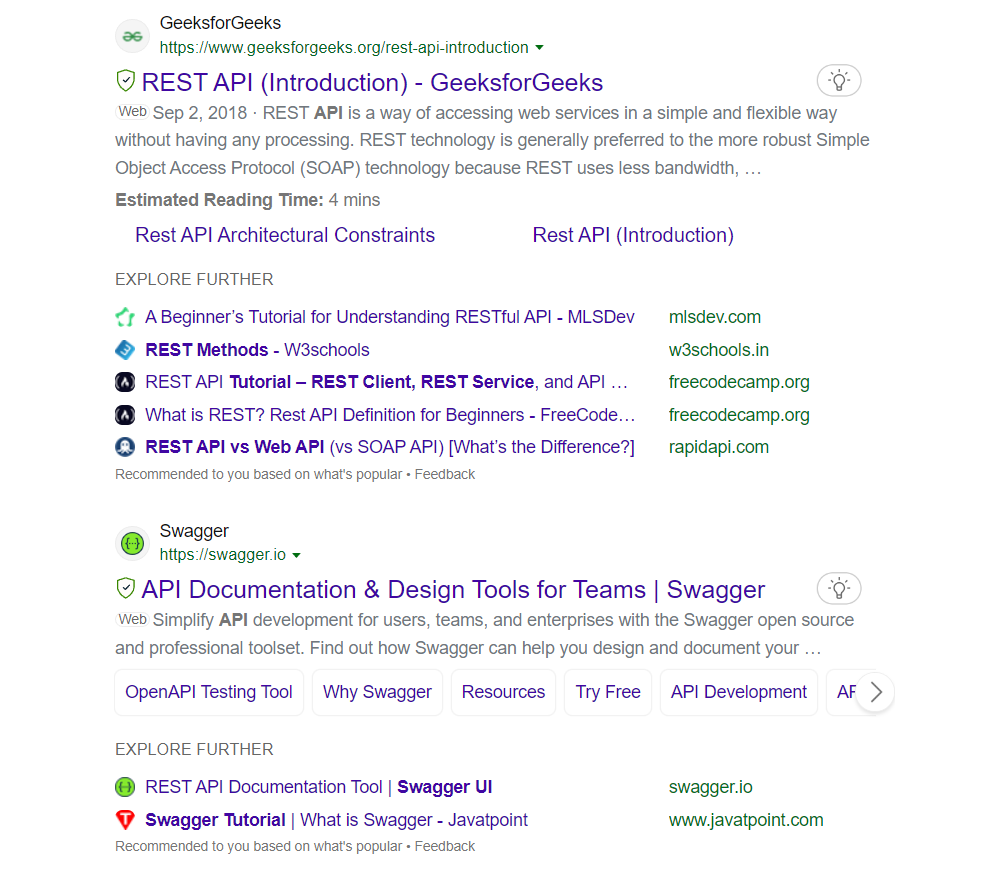
We will start the program by importing the required libraries.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
Next, we will make an HTTP request at the target URL to extract the raw HTML data.
url = 'https://www.bing.com/search?q=api&count=10'
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/104.0.5023.114 Safari/537.36",
}
response = requests.get(url, headers = headers)
To parse this extracted data, we will use the BeautifulSoup library to easily navigate inside the DOM and search for the required HTML elements.
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
Then, we will search for the tags from HTML.
We will extract the title, snippet, and link from the search results.
If you inspect the HTML, you will know that every organic result is under the tag li with class .b_algo.
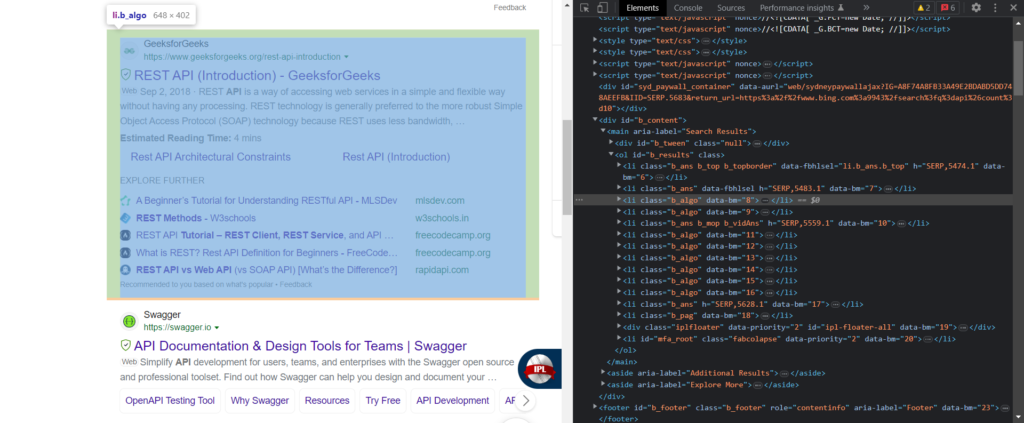
So, we will loop over all these list tags and extract the required information from them.
search_results = []
for result in soup.find_all('li', class_='b_algo'):
Let us now locate the tag of the title.
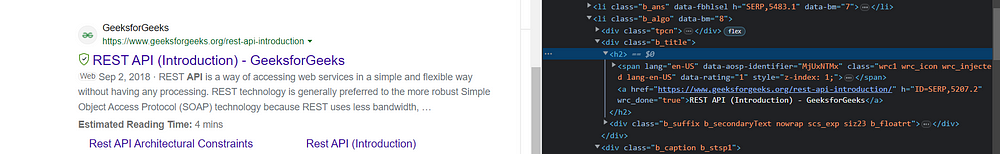
Inside the h2 element, you can find the title. You can also see the link under the h2 tag.
So, let us scrape both things.
for result in soup.find_all('li', class_='b_algo'):
title = result.find('h2').text
url = result.find('h2 a')['href']
And finally, we will locate the tag for the snippet.
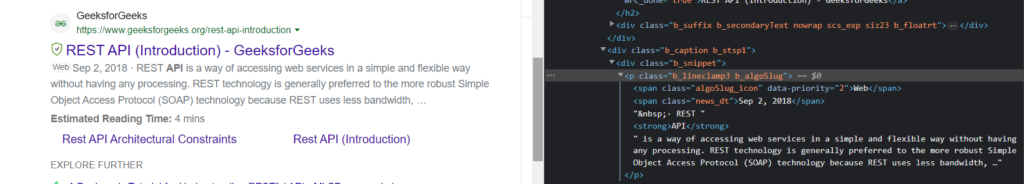
The paragraph with the class b_algoSlug contains our snippet.
for result in soup.find_all('li', class_='b_algo'):
title = result.find('a').text
url = result.find('a')['href']
snippet = result.find('p.b_algoSlug').text
Finally, we will append the parsed data to our search_results array.
search_results.append({
'title': title,
'url': url,
'snippet': snippet
})
print(search_results)
Run this program in your terminal. you will get the expected results.
[
{
'title': 'What is an Application Programming Interface (API)? | IBM',
'url': 'https://www.ibm.com/topics/api',
'snippet': 'WebAn API, or application programming interface, is a set of defined rules that enable different applications to communicate with each other. It acts as an intermediary layer that processes data transfers between systems, letting companies open their application data and functionality to external third-party developers, business partners, and internal …'
},
{
'title': 'What is an API? - Application Programming Interfaces ...',
'url': 'https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/api/',
'snippet': 'WebA Web API or Web Service API is an application processing interface between a web server and web browser. All web services are APIs but not all APIs are web services. REST API is a special type of Web API that uses the standard architectural style explained above. The different terms around APIs, like Java API or service APIs, exist because ...'
},
]
.....
So, this is how you make your basic scraper to extract Bing Search Results.
Here is the complete code:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = 'https://www.bing.com/search?q=api&count=10'
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/104.0.5023.114 Safari/537.36",
}
response = requests.get(url, headers = headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
search_results = []
for result in soup.find_all('li', class_='b_algo'):
title = result.find('a').text
url = result.find('a')['href']
snippet= result.find('p').text
search_results.append({
'title': title,
'url': url,
'snippet': snippet
})
print(search_results)
Problems with Official Bing Search API
There are various reasons why developers do not prefer the official Bing Search API:
Expensive — The official Bing Search API is not budget-friendly for developers. That is why they consider Web Scraping API over it every time.
Limited Features — Bing Search API offers various plans and features, depending on its pricing. However, not all features are included in a single plan. That is why businesses around the globe consider web scrapers, which give them full access to the results.
Complex Setup — It can be difficult for users with nontechnical backgrounds to set up the API.
Scraping Bing Using Bing Search API
Scraping data from Bing is difficult if you are planning to extract data on a large scale. Their anti-bot protection is even stronger than Google’s and won’t allow your IP to keep browsing their website.
But what if we have a cluster of proxies consisting of a large number of residential and data-center proxies?
We will be able to collect data from Bing without any issues!
This can be achieved using Serpdog’s Bing Search API, which has already done most of the work for you. It allows customers to rotate proxies and headers with each request, enabling seamless data scraping from Bing through its robust data pipeline.
Let us take a step forward and try out the Bing Search API by Serpdog by registering on its website.
After registering, you will be redirected to its dashboard to get your API Key.
Copy this API Key, and paste it into the code below.
import requests
payload = {'api_key': 'APIKEY', 'q':'coffee+making+tutorial'}
resp = requests.get('https://api.serpdog.io/bing_search', params=payload)
print (resp.text)
Here we go!!
Simple isn’t it? We didn’t have to write the long code and search for the HTML Tags. Moreover, we got the results more quickly.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned to scrape Bing Search Results using Python. Please do not hesitate to message me if I missed something.
If you think we can complete your custom scraping projects, feel free to contact us. Follow me on Twitter. Thanks for reading!
Additional Resources
- Web Scraping Google With Node JS — A Complete Guide
- Web Scraping- A Complete Guide
- Web Scraping With Python
- Web Scraping Google News Result
- Scrape Zillow With Python
- Scrape Google Search Results With Go

